Installing WordPress on Windows: Part2
Installing WordPress on Windows: Part1
Installing WordPress on Windows: Part3
Installing WordPress on Windows: Part4
In the second part, we will cover PHP installation and configuration.
Some users want to install PHP by using Microsoft Web Platform Installer. I would not recommend it anymore, because we don’t have a choice to install the latest version of PHP. It is better to manual install it. We can download PHP from the site PHP For Windows: Binaries and sources Releases.
In general we have three options:
PHP 7.4.29 (the latest 7.4 build),
PHP 8.0.18 (the latest 8.0 build) and
PHP 8.1.5 (the latest 8.1 build).
After testing all three options, I would recommend using PHP 8.1.5 with the latest WordPress version 5.9.3. We get the fastest response and we don’t get internal server errors 500. Some plugins may not be compatible with PHP 8.1.5, but we can solve the plugins problems by using workarounds.
Be aware, that PHP 8.1.5 has not been officially supported yet.
If you will use PHP 8.0.18, be prepare to get internal server error 500 randomly from time to time.
With PHP 7.4.29, your WordPress Site will be much slower.
For using PHP as FastCGI with IIS, we should use the Non-Thread Safe (NTS) versions of PHP. So we need to download PHP 8.1.5 VS16 x64 Non Thread Safe zip file.
We have to Unzip everything to the selected PHP folder. I choose the C:\PHP folder.
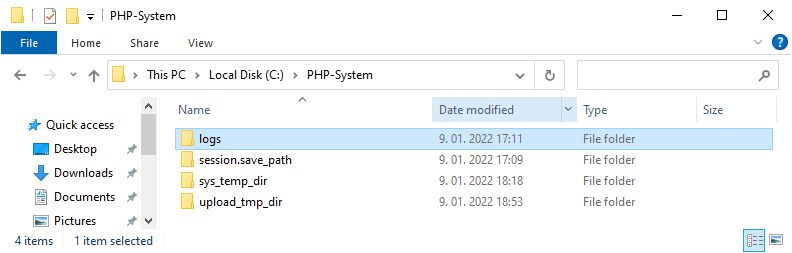
We create another folder, C:\PHP-System, which will be used for temporary and log files. Inside the C:\PHP-System folder, we create 4 folders:
logs
session.save_path
sys_temp_dir
upload_tmp_dir
Inside logs folder, we create an empty PHP_errors.log file.
We also create the folder, C:\PHP-Imagick, which will be used for Imagick extension, that is needed for WordPress. We can download php_imagick-3.7.0-8.1-nts-vs16-x64.zip file. We have to Unzip everything to the C:\PHP-Imagick folder. Then copy the php_imagick.dll file in the C:\PHP\ext folder.
For future upgrades of PHP, we will only replace files in the C:\PHP, C:\PHP-Imagick folders and the php_imagick.dll file in the C:\PHP\ext folder.
Now, we have to duplicate the php.ini-production file in C:\PHP folder and rename it to the php.ini.
In the next step, we have to configure the php.ini for WordPress use. We have to change various parameters in the php.ini file:
587 ; empty.
588 ; https://php.net/error-log
589 ; Example:
590 ;error_log = php_errors.log
591 ; Log errors to syslog (Event Log on Windows).
592 error_log = “C:\PHP-System\logs\PHP_errors.log”
695 ; Its value may be 0 to disable the limit. It is ignored if POST data reading
696 ; is disabled through enable_post_data_reading.
697 ; https://php.net/post-max-size
698 post_max_size = 32M
768 ; Defaults to the system default (see sys_get_temp_dir)
769 sys_temp_dir = “C:\PHP-System\sys_temp_dir”
778 ; most web servers. Left undefined, PHP turns this on by default. You can
779 ; turn it off here AT YOUR OWN RISK
780 ; **You CAN safely turn this off for IIS, in fact, you MUST.**
781 ; https://php.net/cgi.force-redirect
782 cgi.force_redirect = 0
796 ; previous behaviour was to set PATH_TRANSLATED to SCRIPT_FILENAME, and to not grok
797 ; what PATH_INFO is. For more information on PATH_INFO, see the cgi specs. Setting
798 ; this to 1 will cause PHP CGI to fix its paths to conform to the spec. A setting
799 ; of zero causes PHP to behave as before. Default is 1. You should fix your scripts
800 ; to use SCRIPT_FILENAME rather than PATH_TRANSLATED.
801 ; https://php.net/cgi.fix-pathinfo
802 cgi.fix_pathinfo=1
809 ; security tokens of the calling client. This allows IIS to define the
810 ; security context that the request runs under. mod_fastcgi under Apache
811 ; does not currently support this feature (03/17/2002)
812 ; Set to 1 if running under IIS. Default is zero.
813 ; https://php.net/fastcgi.impersonate
814 fastcgi.impersonate = 1
815
816 ; Disable logging through FastCGI connection. PHP’s default behavior is to enable
817 ; this feature.
818 fastcgi.logging = 1
844 ; specified).
845 ; https://php.net/upload-tmp-dir
846 upload_tmp_dir = “C:\PHP-System\upload_tmp_dir”
847
848 ; Maximum allowed size for uploaded files.
849 ; https://php.net/upload-tmp-dir
850 upload_max_filesize = 10M
918 extension=curl
919 ;extension=ffi
920 ;extension=ftp
921 extension=fileinfo
922 extension=gd
923 ;extension=gettext
924 ;extension=gmp
925 extension=intl
926 ;extension=imap
927 ;extension=ldap
928 extension=mbstring
929 extension=exif ; Must be after mbstring as it depends on it
930 extension=mysqli
931 ;extension=oci8_12c ; Use with Oracle Database 12c Instant Client
932 ;extension=oci8_19 ; Use with Oracle Database 19 Instant Client
933 ;extension=odbc
934 extension=openssl
935 ;extension=pdo_firebird
936 ;extension=pdo_mysql
937 ;extension=pdo_oci
938 ;extension=pdo_odbc
939 ;extension=pdo_pgsql
940 ;extension=pdo_sqlite
941 ;extension=pgsql
942 ;extension=shmop
943 extension=php_imagick.dll
1353 ; does not overwrite the process’s umask.
1354 ; https://php.net/session.save-path
1355 session.save_path = “C:\PHP-System\session.save_path”
1767 opcache.enable=1
1768
1769 ; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled for the CLI version of PHP
1770 opcache.enable_cli=0
1771
1772 ; The OPcache shared memory storage size.
1773 opcache.memory_consumption=2048
1774
1775 ; The amount of memory for interned strings in Mbytes.
1776 opcache.interned_strings_buffer=64
1777
1778 ; The maximum number of keys (scripts) in the OPcache hash table.
1779 ; Only numbers between 200 and 1000000 are allowed.
1780 opcache.max_accelerated_files=50000
1781
1782 ; The maximum percentage of “wasted” memory until a restart is scheduled.
1783 opcache.max_wasted_percentage=15
1792 ; webserver for changes to the filesystem to take effect.
1793 opcache.validate_timestamps=0
1794
1795 ; How often (in seconds) to check file timestamps for changes to the shared
1796 ; memory storage allocation. (“1” means validate once per second, but only
1797 ; once per request. “0” means always validate)
1798 opcache.revalidate_freq=0
1804 ; size of the optimized code.
1805 opcache.save_comments=1
1862 ; processes have to map shared memory into the same address space. This
1863 ; directive allows to manually fix the “Unable to reattach to base address”
1864 ; errors.
1865 opcache.mmap_base=0x20000000
We have installed and configured PHP for WordPress. It is done the second step with our installing WordPress on Windows series.
Next, we have to install and configure IIS that use PHP as FastCGI.
Leave a Comment